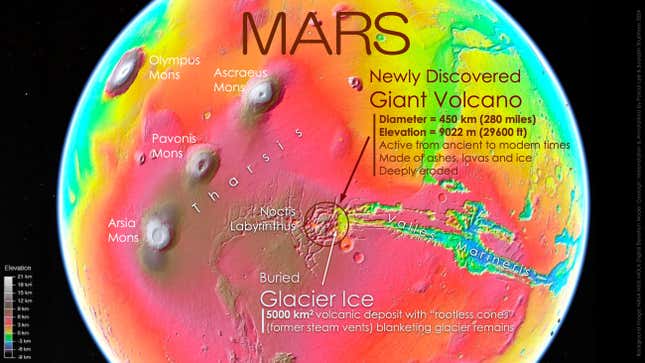
An enormous volcano has been present in Mars’ Tharsis plateau, making it the fourth recognized volcano within the area. Closely eroded, the 29,600-foot (9,022-meter) volcano has been hiding in plain sight, sneaking its mug into photos of the Tharsis area however by no means really being seen. Till now.
The volcano’s discovery was introduced this week on the fifty fifth Lunar and Planetary Science Convention in Texas. Abutting the maze-like geology of Noctis Labyrinthus, the enormous volcano has been provisionally named Noctis Mons. You’ll be able to learn the paper initially describing the invention here. The volcano was discovered with knowledge from a number of Mars orbiters, together with NASA’s Viking orbiters and the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, and ESA’s Mars Categorical orbiter.

“It’s an historic and long-lived volcano so deeply eroded that you possibly can hike, drive, or fly by it to look at, pattern, and date completely different elements of its inside to review Mars’ evolution by time,” Pascal Lee, a planetary scientist on the SETI Institute and the lead writer of the brand new examine, stated in an institute release. “It has additionally had an extended historical past of warmth interacting with water and ice, which makes it a major location for astrobiology and our seek for indicators of life.
The volcano is on the western fringe of Valles Marineris, a vast canyon system on Mars that’s 10 instances longer, 20 instances wider, and 5 instances deeper than the Grand Canyon. It was noticed “hiding close to Mars’ equator in plain sight,” in accordance with the press release. The staff believes the volcano is a protect composed of layered lava, ice, and pyroclastic materials. As faults and fractures fashioned within the volcano, lava rose, inflicting thermal erosion and, in the end, the collapse of swaths of the volcano.
Whereas the newly found volcano simply edges out Mount Everest (29,000 toes, or 8,839 meters) within the peak division, it’s comfortably dwarfed by Mars’ largest volcano, Olympus Mons, which is the scale of Arizona and an imposing 16 miles (25.75 kilometers) excessive.
Final yr, the team found a relict glacier within the geologically younger area, a hopeful signal for future human habitation on a chilly, arid, usually inhospitable world. That discovering was introduced ultimately yr’s Lunar and Planetary Science convention. Upon additional investigation, “we realized we have been inside an enormous and deeply eroded volcano,” Lee stated.
“Lastly, with glacier ice doubtless nonetheless preserved close to the floor in a comparatively heat equatorial area on Mars, the place is trying very enticing for robotic and human exploration,” he added.
If ice have been preserved close to the Martian floor, it might be a compelling venue for human habitation. Methods to produce meals, water, and even air on Mars will likely be crucial issues to unravel if aspirations of human exploration of other planets (and beyond!) is to happen.
Mars’ volcanoes don’t have Vesuvian outbursts—not less than none that scientists have noticed. However the planet is seismically lively: in 2022, the since-decommissioned InSight lander spotted potential signs of magma in seismic knowledge.
Extra: Curiosity Rover Spots Clear Evidence of Ancient Water on Mars
Trending Merchandise

Cooler Master MasterBox Q300L Micro-ATX Tower with Magnetic Design Dust Filter, Transparent Acrylic Side Panel…

ASUS TUF Gaming GT301 ZAKU II Edition ATX mid-Tower Compact case with Tempered Glass Side Panel, Honeycomb Front Panel…

ASUS TUF Gaming GT501 Mid-Tower Computer Case for up to EATX Motherboards with USB 3.0 Front Panel Cases GT501/GRY/WITH…

be quiet! Pure Base 500DX Black, Mid Tower ATX case, ARGB, 3 pre-installed Pure Wings 2, BGW37, tempered glass window

ASUS ROG Strix Helios GX601 White Edition RGB Mid-Tower Computer Case for ATX/EATX Motherboards with tempered glass…










